Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings Guide
| Solids | Water | ||
| 1. | Protected against a solid object greater than 50mm such as a hand. | 1. | Protected against vertically falling drops of water.Limited ingress permitted. |
| 2. | Protected against a solid object greater than 12.5mm such as a finger. | 2. | Protected against vertically falling drops of water with enclosure tilted up to 15 degrees from the vertical.Limited Ingress permitted. |
| 3. | Protected against a solid object greater than 25mm such as a screwdriver. | 3. | Protected against vertically falling drops of water. Limited Ingress permitted. |
| 4. | Protected against a solid object greater than 1mm such as a wire. | 4. | Protected against sprays of water up to 60 degrees from the vertical. Limited ingress permitted for three minutes. |
| 5. | Dust protected. Limited ingress of dust permitted. Will not interfere with operation of the equipment. Two to eight hours, | 5. | Protected against jets of water. Limited ingress permitted. |
| 6. | Dust tight. No Ingress of dust. Two to eight hours. | 6. | Water from heavy seas of water projected in powerful jets shall not enter the enclosure in harmful quantities. |
| 7. | Protection against the effects of immersion in water between 15cm and 1m for 30 minutes. | ||
| 8. | Protection against the effects of immersion in water under pressure for long periods. | ||
| 9. | Protection against the effects of high pressure and temperature waterjet. | ||
Calling something “waterproof” or “dust-resistant” isn’t really very useful. After all, it’s difficult to know exactly what that means in terms of how an electrical enclosure or mechanical casing will protect against dust, water, and other potentially damaging objects, such as screwdrivers or wires.
That’s why the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) created its IP rating system of standards in 1976. The IEC 60529 standard, prepared by IEC Technical Committee 70, uses the IP code to rate the degree of protection offered by an electrical equipment enclosure.
What Is the IP Rating System?
The IP rating system is a set of international standards for quantifying the degree of protection provided by electrical enclosures and mechanical casings against the ingress of solid foreign objects and water. The standard also defines tests to be performed to verify that an enclosure meets those requirements.
Though typically assigned to enclosures such as circuit boxes and locker-like chambers that hold automation controls, IP ratings are also applicable to connectors, interconnect products, and motion system components such as linear actuators.
How Engineers Use IP Ratings
IP stands for “ingress protection” or sometimes “international protection.” An industrial computer’s IP rating quantifies how resilient it is to intrusions such as dust and water. Engineers often present IP standards in the form of a table, which provides a convenient and practical way to compare levels of sealing.
When choosing industrial control components, the goal is to select components with IP ratings that will suitably deliver the level of quality, safety, and service life required for the operating environment in which the application must function.
Explaining the Two-Digit IP Code
The IP code is composed of two numbers. The first refers to the level of protection against solid objects on a scale from 0 (no protection) to 6 (no ingress of dust). The second number rates an enclosure’s protection against liquids on a scale from 0 (no protection) to 9 (protection again water under high pressure coming from different angles).
IP Rating Tables
Below are two tables that specify what the numbers in an IP rating mean. Table 1 rates solid protection, and Table 2 rates liquid protection.

Table 1: Solid Protection
| First Digit | Size of Object Blocked | Effective Protection |
| 0 | n/a | No protection against con tact and ingress of objects |
| 1 | > 50 mm | Protection against any large surface of the body, such as the back of a hand, but no protection against deliberate contact with a body part |
| 2 | > 12.5 mm | Protection against fingers and similarly sized objects |
| 3 | > 2.5 mm | Protection against tools, thick wires, and similar objects |
| 4 | > 1 mm | Protection against most wires, screws, and other small objects |
| 5 | Dust-protected. Ingress of dust Is not entirely prevented, but dust cannot enter in sufficient quantities to Interfere with the satisfactory operation of the equipment; complete protection against contact. | |
| 6 | Dust-tight. No Ingress of dust; complete protectlonagalnst contact. |

Table 2: Liquid Protection
| Second Digit | Protection Against | Effective Protection |
| 0 | Nothing | none |
| 1 | Dripping water | No harm from vertically falling drops of dripping water |
| 2 | Water dripping at IS’ tilt | Vertically dripping water will have no effect when enclosure Is tilted at 15° |
| 3 | Spraying water | No detrimental effects from water falling asa spray at any angle up to 60’from vertical |
| 4 | Splashing water | No harmful effects from water splashing against enclosure from any direction |
| 5 | Waterjets | No detrimental effects from water projected by a nozzle against the enclosure from any direction |
| 6 | Powerful water jets, and temporary submersion | Protected against temporary flooding of water, e.g. for use on ship decks -limited ingress permitted. |
| 69K | High pressure waterjetsand high temperature | Protected against ingress of high temperature (steamj/hlgh pressure water, |
| 7 | Full Immersion | Protected against Ingress of high temperature (steam)fhlgh pressure water, |
| 8 | Full Immersion at higher pressures and depths | Protects against long periods of immersion under pressure. |
IP Rating Letter Classifications
IP ratings may include a third designation, which is often a letter. Letters indicate additional protections that an electrical equipment enclosure offers. Table 3 breaks down these letters and their various meanings.

Table 3: The Meaning of Letters in IP Ratings
| Letter | Meaning |
| D | Wire |
| F | Oil-resistant |
| H | High voltage |
| M | Device moving during water test |
| S | Device standing still during water test |
| W | Weather conditions |
What Does the K in IP69K Mean?
The letter K is not specified in IEC 60529 but rather in the German standard DIN 40050-9, which extends the IEC 60529 system with an IP69K rating for high-pressure, high-temperature washdown applications. Enclosures with this rating must not only be dust-tight (IP6x) but also must be able to withstand high pressure and steam cleaning.
IP69K was developed for heavy vehicles that need frequent cleaning (such as cement mixers) but also finds use in other industries, including food processing and other businesses that require a high level of hygiene and cleanliness. IP69K compliance provides protection against dust, high temperatures, chemicals, and high-pressure water.
IP Rating Examples
Industrial computers offer much higher levels of protection against environmental factors than consumer-grade PCs. VenBOX iPC can achieve an IP20 rating on almost any computer by using port covers. Industrial computers are not only more robust but also much more suitable for harsh environments. Many are fully dust-proof, which means they have the IP6x rating.
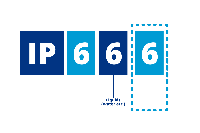
When it comes to water protection, there are several variations. The most common IP ratings for industrial computers are IP55, IP65, IP66, IP67, IP69, and IP69K.
IP65 computers are the standard for industrial applications; IP69K is the maximum level of protection currently available on the market.
Here is a rundown of the most common IP ratings for industrial computers and the type of protection that each offers:
- IP55: Protection in dusty environments with some water
- IP65: Dust-proof; protected from splashes and low-pressure jets
- IP66: Dust-proof; protected from strong waterjets
- IP67: Dust-proof; protected from temporary immersion in water 1 meter deep for 30 minutes
- IP68: Dust-proof; protected from continuous immersion in water under more severe conditions
- IP69K: Dust-proof; protected from water during high-pressure and steam cleaning (not submersible)
 Majority of VenBOX iPC and POS equipment have IP55 and protection. IP64, IP65, IP66, IP67, and IP69 protection are offered in Industrial mini PC series. All these industrial computers feature tough enclosures designed to protect the hardware across a range of challenging environmental conditions.
Majority of VenBOX iPC and POS equipment have IP55 and protection. IP64, IP65, IP66, IP67, and IP69 protection are offered in Industrial mini PC series. All these industrial computers feature tough enclosures designed to protect the hardware across a range of challenging environmental conditions.
The Benefits of IP69K Industrial Computers
An IP69K-rated industrial computer enclosure protects against dust, moisture, high-pressure water and steam, and high temperature. IP69K compliance is typically required for applications where equipment must be regularly sanitized. Industrial computers with an IP69K rating can withstand severe high-pressure and high-temperature washdowns and are extremely durable and resistant in harsh environments.
How Do Industrial Computers Achieve the IP69K Rating?
IP69K compliance requires rigorous testing by a team of professional engineers under very strict conditions. Enclosures with this rating withstand a rigorous high-pressure washdown procedure while rotating on a turntable at 5±1 revolutions per minute. During the rotating water intrusion test, the product is sprayed at close range at a rate of approximately 4 gallons per minute with the water pressure between 1160 and 1450 psi and at a temperature of 80°C. The spray nozzle is held 4-6 inches from the product enclosure at a variety of angles.
Conclusion
IP ratings have a significant impact on the service life and performance that an industrial computer can deliver in a given operating environment. IP ratings have a significant impact on industrial computer performance, business profitability, and overall success. Buying industrial computers with the proper IP rating not only maximizes equipment utilization but also can save a business thousands of dollars in unnecessary equipment downtime and repairs, ensures that critical manufacturing tasks are completed on time.
Please contact our knowledgeable and experienced staff at sales@VenBOX.com or +48 22 188 18 55 for answers to your IP rating questions and help in selecting the most suitable IP rating for your industrial computer application.