Our article is intended for users who are considering upgrading Windows or are unable to upgrade to Windows 11 because TPM 2.0 is not enabled or set on their computer. We invite you to read on.
1. What is a TPM module?
2. Microsoft security requirements.
3. How can I tell if my computer already has a TPM module?
4. Can I install Windows 11 without TPM 2.0?
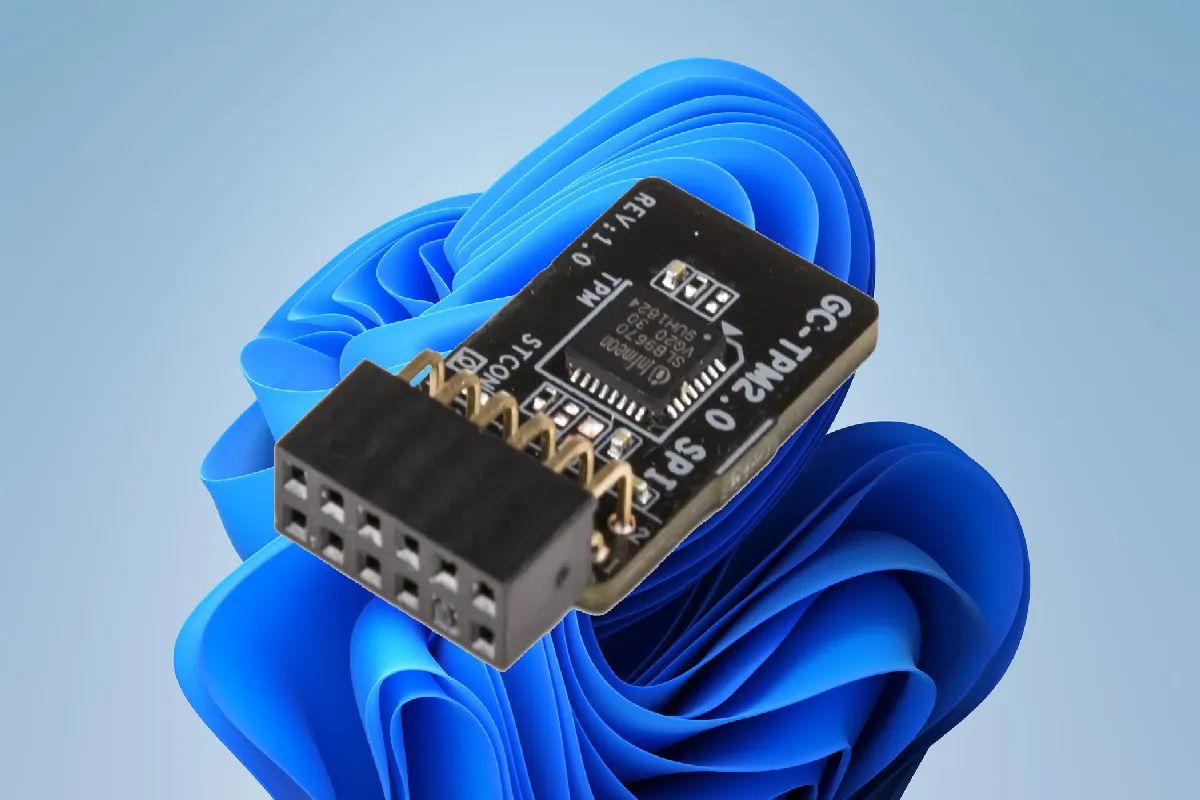
A TPM, or Trusted Platform Module, is a physical or embedded security technology (microcontroller) located on a computer's motherboard or processor. TPM modules use cryptography to help securely store essential and critical information for platform authentication on the computer. They store various sensitive information—such as user credentials, passwords, fingerprints, certificates, encryption keys, or other important individual user documentation—behind a hardware barrier to protect it from external attacks.
While TPM technology has been used in enterprise computing environments for over a decade, this is one of the first times Microsoft is requiring its use by everyone, including small and medium-sized businesses and consumers.
TPM implementations are designed to meet the international standard created by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG). The TCG is a computer industry consortium that created the original TPM standard, which was later adopted by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and subsequently named ISO/IEC 11889.
The TPM module generates and stores parts of the encryption keys for computers.
Microsoft, when releasing the new version of Windows 11, is focusing on a high level of security. In the previous version, TPM was not required, but now it is. Why? Microsoft is particularly focused on supporting modern, stronger cryptographic algorithms. Secondly, TPM 2.0 is part of the Secured-core PC standard. Computers with this certification are much more protected against firmware attacks. And these types of attacks are more common than you might think. These days, our cybersecurity is constantly at risk. Hackers are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Attacks are gaining momentum, and the shockingly high costs associated with cybercrime and security breaches can easily lead to the collapse of a company. For companies that want to meet these challenges and ensure their security, updating to TPM2.0 is essential.
How can I tell if my computer already has a TPM module? If my computer is less than 5 years old, it should have a TPM 2.0 module. You can check this as follows:
a) Go to Start -> Settings -> Updates & Security -> Windows Security -> Device Security. If you have it, you'll also see a Security Processor section on your screen.

The next step is to determine which TPM version your computer is using. Select Security Module Details and look for Specification Version on the screen that appears. It should be "1.2" or "2.0." If you don't see the Security Processor section, your device may have a TPM, but it's disabled. The Windows 11 specification requires a minimum TPM version of 2.0. Learn how to enable the TPM service for more information, or check your computer manufacturer's support information for instructions.
b) After typing tpm.msc in the search box on the Windows Start bar, a box titled "Manage TPM on your local computer" will appear. Then, in the "Status" section, you should see information that the TPM module is ready for use.

Can Windows 11 be installed without TPM 2.0? Yes, as other users who found information provided by the system manufacturer have already discovered. Microsoft emphasizes that it does not recommend installing the new system on a computer that does not meet the requirements. It also encourages contacting technical support before installation. How do I update Windows 11?
First, make sure the TPM module is activated in the BIOS. The path depends on your computer and BIOS version. If it is enabled, start the system and open the registry editor (Win+R -> regedit), then go to:
· HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup\MoSetup.
· Right-click the registry editor window and select New, then DWORD (32-bit value).
· Name it AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPMorCPU.
· Then change its value to 1.
· You should then be able to upgrade to Windows 11 without TPM 2.0.
If the information in this article was helpful, we encourage you to share your feedback.
Sources:
https://support.microsoft.com/pl-pl/windows/w%C5%82%C4%85czanie-tpm-2-0-na-komputerze-1fd5a332-360d-4f46-a1e7-ae6b0c90645c
https://www.intel.pl/content/www/pl/pl/business/enterprise-computers/resources/trusted-platform-module.html
https://www.centrumxp.pl/Publikacja/TPM-20-w-Windows-11---czym-wlasciwie-jest
https://support.microsoft.com/pl-pl/topic/co-to-jest-modu%C5%82-tpm-705f241d-025d-4470-80c5-4feeb24fa1ee
https://www.computerworld.pl/news/TPM-czy-rzeczywiscie-potrzebujemy-TPM-2-0-do-Windows-11,430753.html
https://gamingsociety.pl/artykul/windows-11-microsoft-pokazal-jak-obejsc-wymaganie-tpm-2-0-1133326/