The article is devoted to DLNA - a technology that is currently actively used, and its popularity has gained with the increasing use of Smart TV. So -
The article is devoted to DLNA - a technology that is currently actively used, and its popularity has gained with the increasing use of Smart TV. So -
What is DLNA?
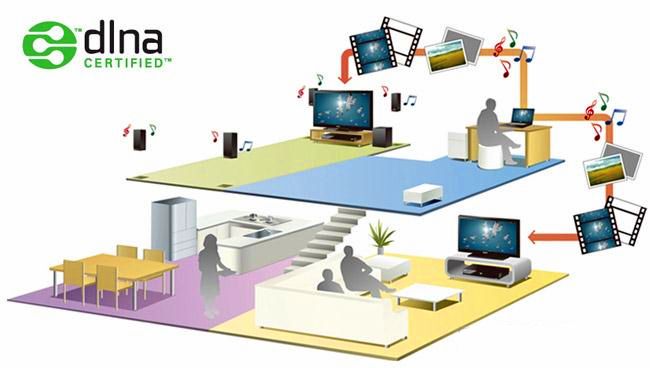
DLNA is a specific technology enabling quick transfer of content between hardware media, organized in a home group. Compatible devices of this standard enable real-time playback of large amounts of files from remote storage, especially music, video, and photos. This is very convenient, as this solution opens up access to collections and archives on a new page, ensuring the most comfortable work with content.
DLNA technology is a unique, intelligent, next-generation solution because it usually performs most operations quickly, and network settings are almost completely automatic, ignoring the complexity and number of communication participants. The basis for the operation of such solutions is an operating environment that can be both wired and wireless, based on Wi-Fi capabilities. A typical option is a local IP network that connects all devices into a single system and assigns each element its own address.
Scope and main features
The basis of the standard is UPnP technology, which ensures a reliable connection and stable operation with any data stream, regardless of format. The network can connect various devices: TVs, mobile phones, media players, and other types of modern electronic devices. The transport protocol in this case is TCP / IP. DLNA is a mandatory feature in the latest PlayStation and Xbox models. Currently, there are approximately over 200 manufacturers in this niche. The technology is constantly being updated, becoming faster and more accurate.
To implement standard support on a regular PC, all you need is the right program, so the choice is quite large, from Windows Media Player 12 to sophisticated media servers like MythTV, managing almost any exchange scenario and flow path. Windows Media Connect allows you to work with this technology even in quite old solutions with the XP platform.
Typical processes of working with DLNA are very clear, and all devices are divided into three classes for convenience:
- Networked home devices, i.e. printers, TVs, players and network storage;
- Portable devices: phones, tablets, laptops or video cameras;
- Special multifunction devices, this is equipment supporting additional communication standards that mediate operation via a DLNA server.
Accordingly, data streams can move between these classes, the task is only to ensure compatibility and stability of the connection.
Network architecture and settings
The structure in the framework of using such technologies can be constructed in different ways, but its general principles are uniform and suitable for different situations. The heart of the system is a DLNA server, the role of which varies depending on the device.
Usually, in a typical home, this plan is much simpler and comes down to a router, laptop, TV, and mobile phone.
In some cases, you can use a dedicated router or home computer, but the best solution is a NAS (network attached storage) device. This is essentially a type of computer designed solely for storing and exchanging data. Devices on the network are managed, often even via a browser.
DLNA is the name of the technology of many multimedia equipment manufacturers: Samsung called it AllShare, LG - SmartShare, Philips and its Simple Share turned out to be not so original, Apple called the standard AirPlay.
In order for devices on the network to be shared, it is necessary to open the necessary folders for their display and use through the created structure. You should immediately move all these files to standard Windows libraries in the "My Documents" group on the system drive, the server will start searching for content exactly there.
When you first connect each new device to the network architecture, you need to have the new device find the appropriate paths to the servers. If this does not happen, the problem may be in the software. Among the most popular and popular samples of suitable software can be called Plex, Twonky, and TVersity. When everything is properly selected from the point of view of compatibility of network elements, the search and exchange of content is carried out at high speed and automatically.
Possible difficulties:
- All codecs and all resolution options do not always work. Problems with playing in FullHD are especially likely.
- Currently, wired networks are more reliable than wireless networks, because in some cases they lose bandwidth.
- Experienced users notice the limitations of some devices in motion, for example, Sony Bravia series TVs do not perceive a stream of more than 15 Mbps.
- Today, phones supporting DLNA technology have many limitations in work.